BLOCKCHAIN TECHNOLOGY
BLOCKCHAIN TECHNOLOGY
Information technology, a sub-discipline of computer science is enormously dynamic. We are in an age where information technology is being used extremely to store, record, and disseminate information in digital form. Nevertheless, it is essential to keep all data safe. To give an illustration of what I mean, blockchain technology is the safest way to secure data from hacking. One of the prominent examples of blockchain technology is “bitcoin”.
The origin of blockchain technology moved to 1991. However current blockchain technology was created in 2008 by an unknown group under the pseudonym “Satoshi Nakamoto”. Bitcoin is the simplest way to understand what is blocked chain technology. From recent updates, bitcoin is more worth than 18,091usd.
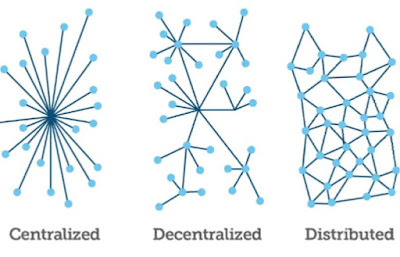
Blockchain technology is a decentralized distributed ledger based on peer to peer (P2P) topology. Another key thing to remember is in blockchain technology allows data to be stored globally on “nodes”. Nodes are the places that the theoretical blockchain exists. A full node is basically a device that contains a full copy of the transaction history of the blockchain. In nodes, there’s a block. Blockchain is produced by a growing list of records called blocks. Each block contains a cryptographically hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transactions data. Another key thing to remember is that a blockchain protects against malicious attempts to alter data by hackers.
World’s biggest blockchain company is IBM which is one of the world-leading American multinational technology company. There are free resources to learn blockchain. Blockchain by IBM etc.
Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that there are a lot of advantages of blockchain technology High level of security, Hacking threats reduced, faster transactions and transparency of transactions increased, etc.
Finally, as with any technology, there are some risks to blockchain technology. Some of them are a risk with the private and public key, vendor risks, untested code, regulatory risks, and human-related risks, etc.






Nice job 👌. Keep up the good work👍
ReplyDelete